
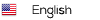

Research
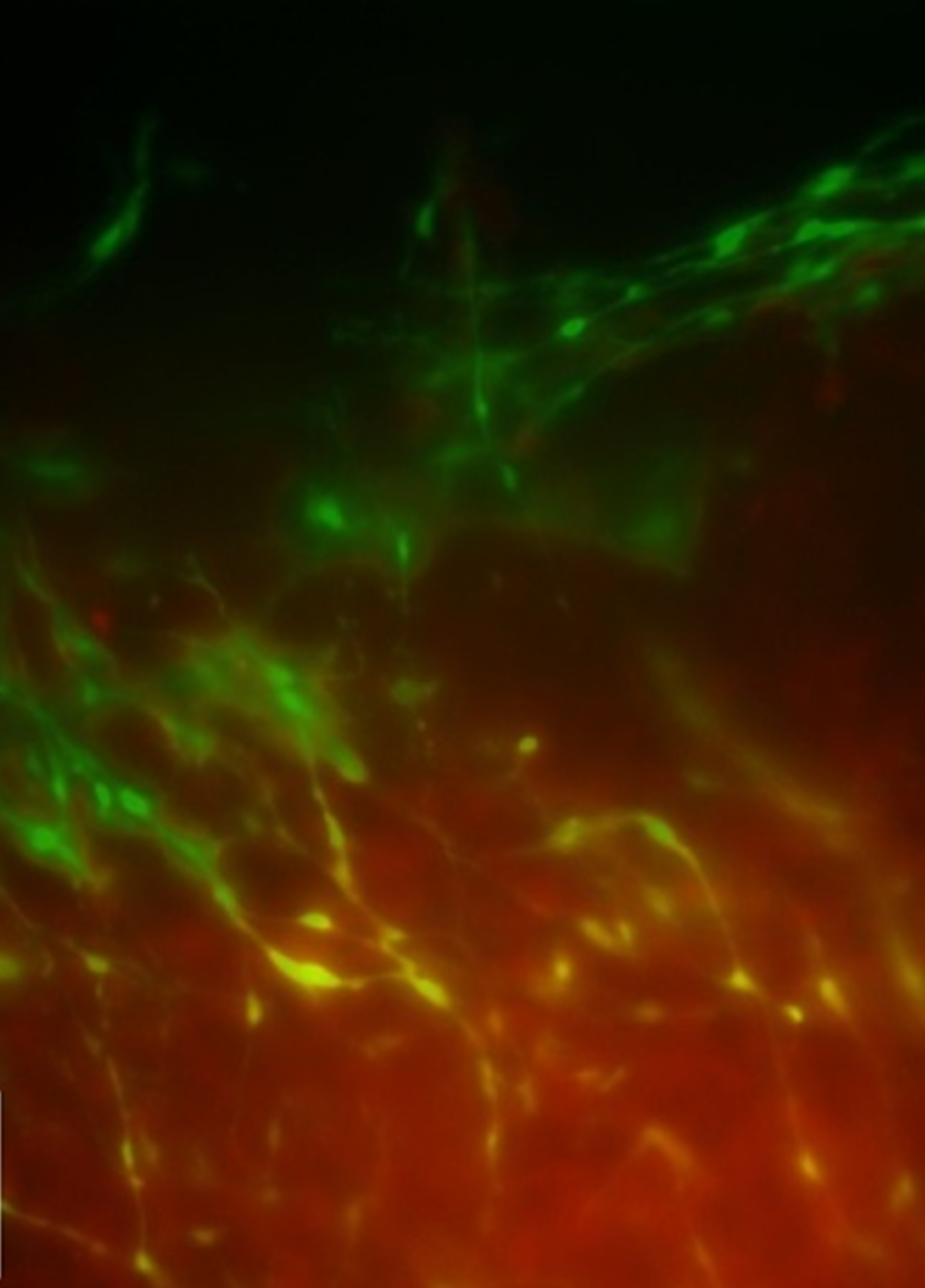
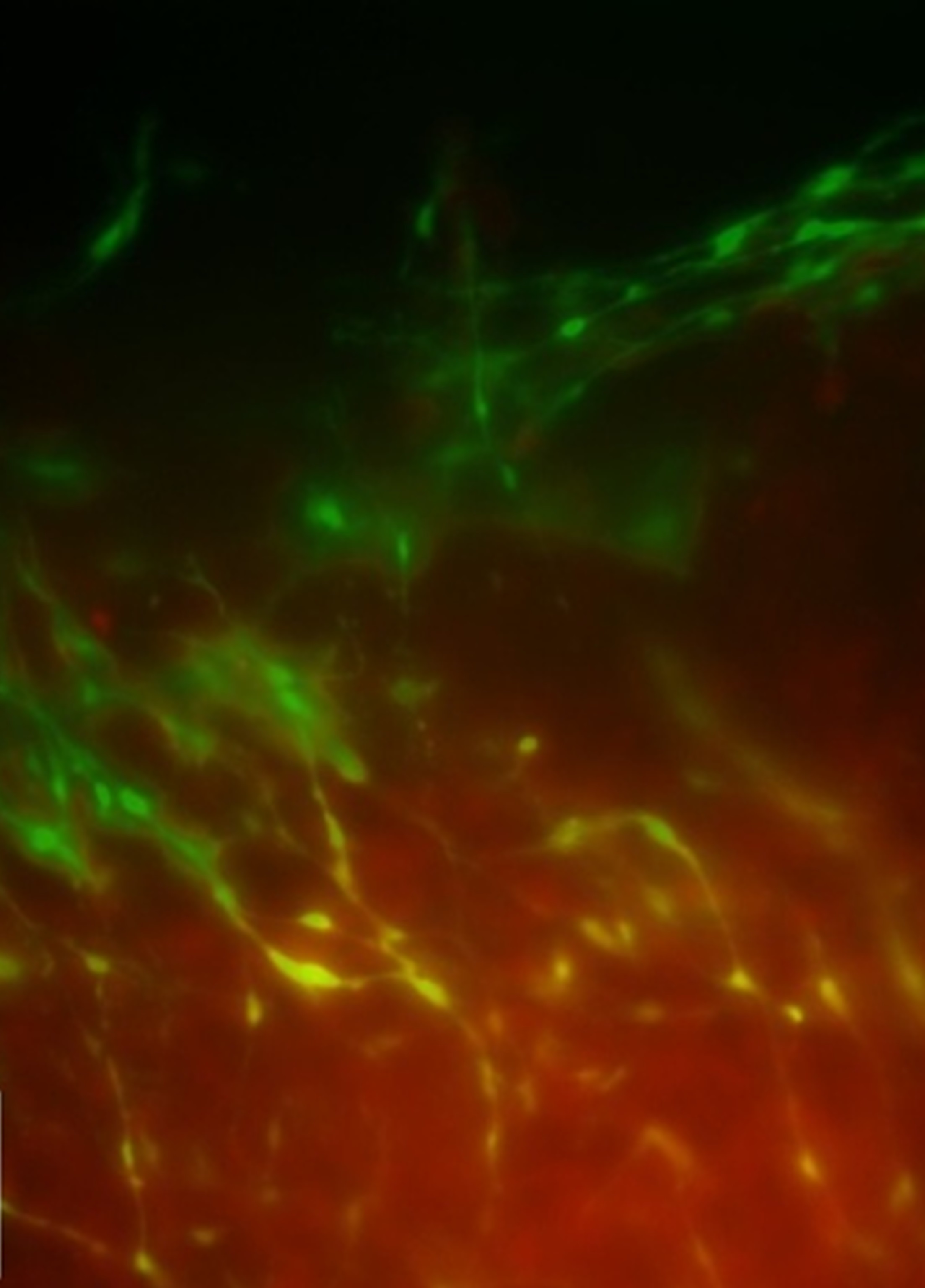
 Fluorescence imaging of a brain section showing that intracranially injected GFP+ NLSCs (green) migrate toward orthotropic GBM tumors in vivo.
Fluorescence imaging of a brain section showing that intracranially injected GFP+ NLSCs (green) migrate toward orthotropic GBM tumors in vivo.
THERAPEUTIC EXPLORATION OF A NEWLY ISOLATED NEURAL-LIKE STEM CELL AGAINST GBM
Glioblastomas are rapidly fatal and
kill close to 14,000 patients annually in the US alone. The goal of this project
is to therapeutically exploit a newly isolated pure population of neural-like
stem cells (NLSCs) that we recently derived from skeletal muscle pericytes and
can thus potentially be a source of autologous transplantation. We are testing
the use of novel stem cell-based therapies to deliver therapeutic agents
specifically to tumor cells but not to the surrounding normal brain tissue.
This approach offers hope against GBM, an invariably fatal disease. Thus, this
project has strong translational relevance.
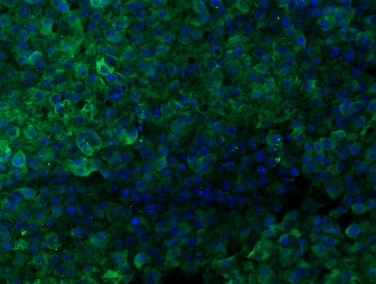
 Presence of GFAP + cells in the Hi-Myc tumor microenvironment. Representative prostate immunofluorescence images of 20-week-old Hi-Myc mice. The white arrow shows the presence of labeled GFAP + cells
Presence of GFAP + cells in the Hi-Myc tumor microenvironment. Representative prostate immunofluorescence images of 20-week-old Hi-Myc mice. The white arrow shows the presence of labeled GFAP + cells
Appreciation of the influence of Schwann cells on tumorogenesis and tumor progression of mice affected by breast cancer
Breast cancer is a malignant neoplasm that mainly affects women, and is also one of the leading causes of cancer death in the world. Schwann cells have already been identified in the microenvironment surrounding tumors. The aim of this project is to evaluate the influence of these cells in progression and development of breast tumor. This research will expand our knowledge about cancer and its interaction with the microenvironment around it. Moreover, it can reveal a new target for treatments against cancer. Thus, this project is extremely relevant.

Comparison of the genetic expression between pericytes of normal and tumoral prostates using Hi-Myc transgenic mice
The major aim of this study is to evaluate the role of vascular stem cells (pericytes) in the microenvironment of prostate tumors. Prostate cancer is the most incident type on the male population, having killed more than 13,000 men in Brazil in 2013. Having that in mind, we are going to compare the genetic profiles of pericytes in prostates with and without cancer, thus enriching the knowledge about cancer development and progression, and applying this knowledge in the pursuit of new molecular targets and innovative therapies against this disease.
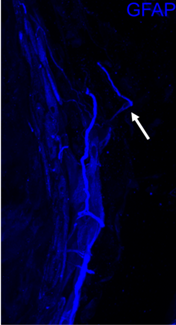
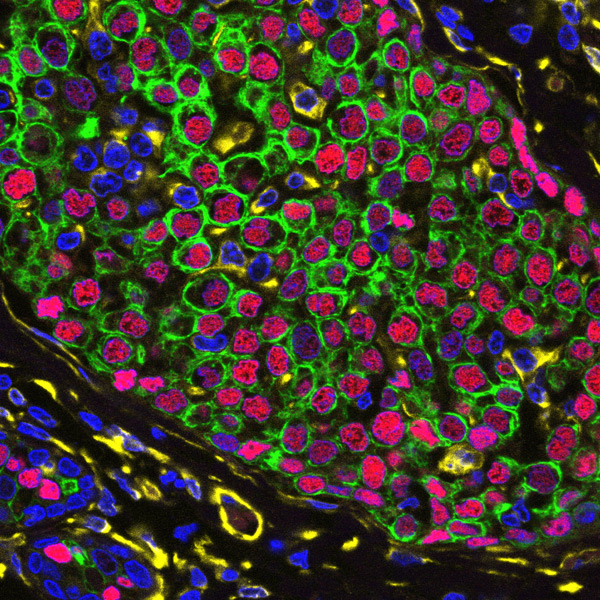 A formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded section of a breast cancer positive for estrogen receptor (ER). An area of ductal carcinoma shows high-resolution four-color immunolabeling after in situ staining fo
A formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded section of a breast cancer positive for estrogen receptor (ER). An area of ductal carcinoma shows high-resolution four-color immunolabeling after in situ staining fo
How does the use of probiotics in the diet prevent breast cancer?
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer breast cancer is the most common tumor in women, which caused 522,000 deaths in 2012. The goal of this project is to identify probiotic bacterias, usually used in food industries, and verify if its installation in the organism modifies the microenvironment of the breast tumor. It is known that some of these bacteria can inhibit cell proliferation, thus this research allows to relate how a diet rich in probiotics helps in cancer prevention.
Study of Pericytes in a Cerebral Ischemia
Cerebral ischemia is one of the most common causes of disability with aging and, according to the WHO, led to 3 million deaths in 2011. Therefore, this project aims to analyze the behavior of multipotent cells, the pericytes, in front of this lesion. Pericytes are perivascular cells with high differentiation capacity, and their performance may be determinant for the lesion picture. Knowing its role is fundamental in order to develop a possible therapy for this condition.
Influence of sensory neurons on the taxonomic composition of the intestinal microbiota
Currently, its understood of a relationship between the intestinal microbiota and the nervous system (NS), where the SN has the ability to modulate the microbiota, as well as the inverse. It is known that intestinal microbiota can interact directly with nociceptive neurons, however, additional studies are needed on the relationship between sensory neurons and intestinal microbiota. Therefore, the objective of this project is to evaluate if the sensory neurons can regulate or affect the taxonomic composition of the intestinal microbiota. From this study it will be possible to understand the role of the association between sensory nerves and microbiota, besides establishing relations with pathologies related to sensory neurons.
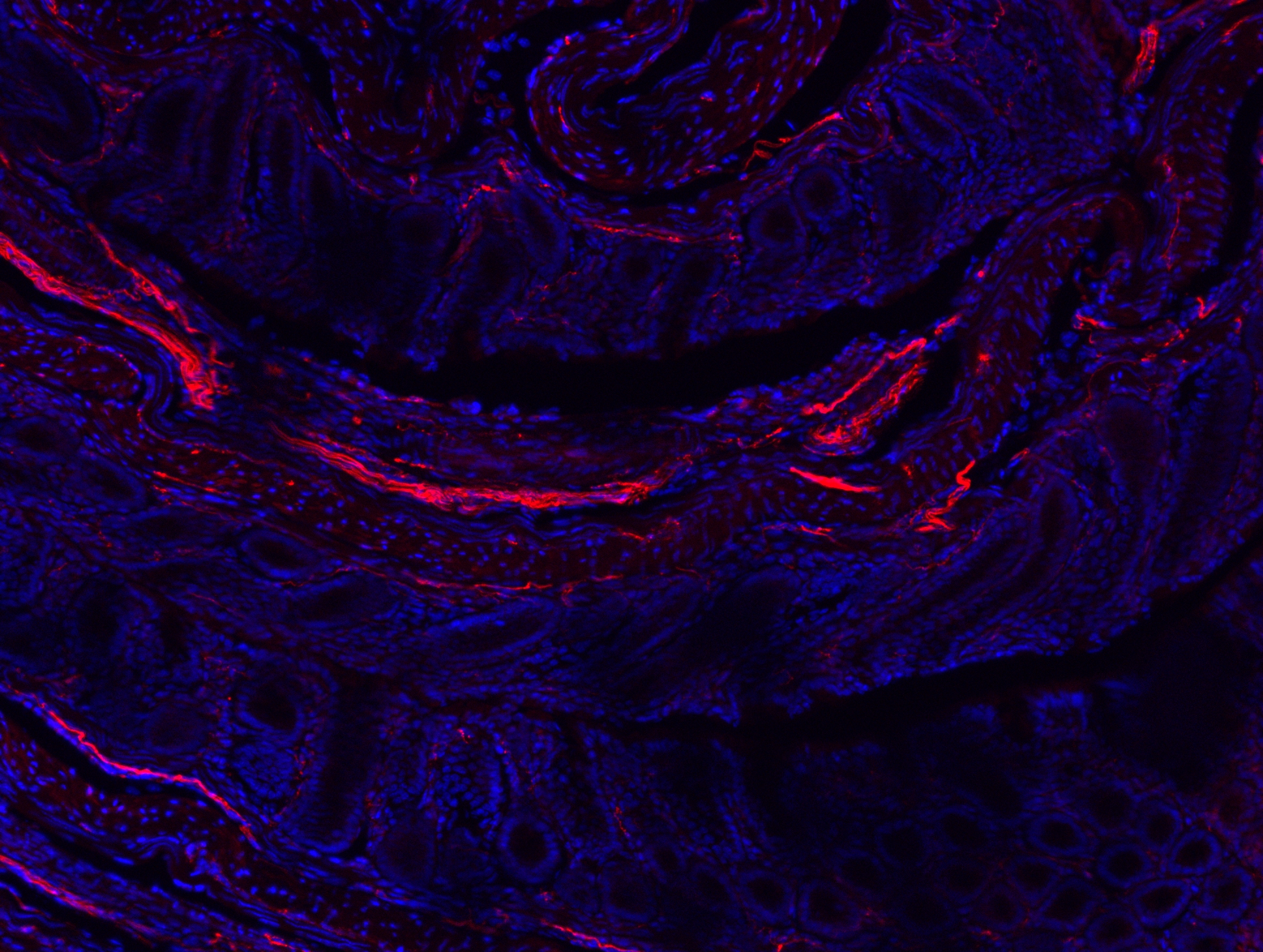
Influence of sensory neurons on the composition of intestinal microbiota
Birbrair Lab © All rights reserved.